What Is A Subdomain?
A subdomain is an additional element added to the start of a website’s domain name. In blog.example.com, “blog.” is the subdomain. Subdomains are usually added to domains to create new pages that have unique content and/or functionality that extend the reach and purpose of a website.

More About Subdomains
Subdomains are an interesting and important piece of the detailed puzzle that makes up domains. And, they can have big benefits for website owners and users alike when implemented thoughtfully and correctly.
In this detailed guide to subdomains, we’ll help you get started with that implementation as well as explore the relationship between subdomains and domains, how subdomains and subdirectories compare and which to choose, the role of subdomains in SEO, when to use subdomains, and even some best practices to make sure you’re using all this newfound knowledge to its fullest potential.
What Is A Subdomain?
A subdomain is an additional element added to the start of a website’s domain name. In blog.example.com, “blog.” is the subdomain.
Subdomains are usually added to domains to create new pages that have unique content and/or functionality that extend the reach and purpose of a website.
What Is The Difference Between Domain And Subdomain?
To really understand a subdomain, it’s helpful to first understand the domain to which it is closely related.
Typically, a domain (or root domain, to be more precise) has two components:
The second-level domain (SLD): This part of a URL usually represents the unique name of the website. Here on our website, “dreamhost” is the SLD.
The top-level domain (TLD): This comes after the SLD and is denoted by suffixes like .com, .edu., etc. At dreamhost.com, that’s “.com.” TLDs help group websites based on country, goal (educational vs. commercial), and type of business or service.
There are tons of types of TLDs:
- Generic top-level domains (gTLDs): .com, .org, .net
- Country code top-level domains (ccTLDs): .uk, .ca, .fr
- New top-level domains (nTLDs): .agency, .bio, .charity
- Sponsored top-level domains (sTLD): .google, .apple
- Government and military TLDs: .gov is limited to U.S. governmental use and .mil to divisions of the U.S. Dept. of Defense
Related reading: Choosing The Perfect Domain Extension For Your Business
That brings us to another part of a domain: the subdomain. The subdomain “belongs” to the root domain but exists outside of it, and is what you see most often before the SLD (but note that sometimes it can come after the TLD).
The most common subdomain is “www.” The “www.” in a domain’s name is from a time when websites weren’t the primary thing we accessed via the internet. To reach an email server, you might have typed in “email.example.com.”
Today, “www.” is by far the default for accessing resources across the internet. It’s so ubiquitous that most domain registrars — the orgs. that sell domain names to people and businesses, and attach IP addresses to them — include this subdomain by default with a domain name purchase. Usually, you can create as many additional subdomains as you like for your website. Costs can vary, but DreamHost (one of ICANN’s accredited registrars) offers free subdomains with many of its hosting plans.
Related: What Is A Web Host?
For websites that haven’t added any additional subdomains, “www.” is the subdomain where all of its pages live. For websites with a subdomain, such as “store.example.com,” all pages associated with that website’s store will live under the “store.” subdomain.
Is A Subdomain The Same As A Child Domain?
Just like the daily languages we speak to each other shift over time to match new realities, trends, and contexts; so does the language used to describe the parts of the internet.
And yes, that was just a really deep way to preface the fact that we don’t have a concrete answer here.
Some argue that a child domain is unique from a subdomain in that it’s more closely related to the “parent domain,” meaning it’s more limited in what it can do but also more secure. But in our experience and according to many other sources, the terms subdomain and child domain can be used interchangeably.
If you’re not sure about this, consult your host and/or domain name registrar to make sure you’re setting up what you think you’re setting up when you create — or ask them to generate — a subdomain.
What Is A Subdomain Example?
As mentioned above, for the website blog.example.com, “blog.” is a subdomain.
If that website serves multiple countries, it may also have other subdomains that look something like “language.example.com.”
Amazon provides a good real-life case study of several subdomains in action.
Their subdomain “aws.amazon.com” tells visitors this section of the website is all about their cloud computing offerings. Then there’s “music.amazon.com” which features the ecommerce platform’s music streaming and sales platform.
Over the next few sections, we’ll talk about why many brands and businesses may choose to use subdomains similarly to the way Amazon does.
The Purpose And Benefits Of Subdomains
At their core, subdomains offer a way for you to structure different areas of your website based on what kind of content and functionality they offer to visitors.
This is helpful from a user experience (UX) standpoint as a person who chooses to visit “blog.example.com” is probably prepared to spend some time reading through long-form content to gain knowledge. But a person who visits “store.example.com” is likely mentally ready to make a purchase, and that unique URL gives them a frictionless way to do so. No need for a visitor to shuffle through endless pages and navigation menu items when they can navigate directly where they want to go with the help of subdomains.
It’s also great for website owners and managers, because subdomains provide a way to create “rooms” within your website. Different rooms will have different features and content, and therefore different upkeep needs. Clearly separating and labeling each room can help you structure a maintenance plan for keeping every area of your website fresh without overwhelm, overwriting, or rework.
Subdomains are also critical for keeping all your seemingly-disparate content together in one place, without the downside of cluttering up the main body of your site, causing confusion to search engines and users alike.
Running a really great month-long sale you want to drive search engine traffic to, but don’t want it to take over your website? Why not set up fallsale.example.com?
Own a few sub-brands that you don’t necessarily want to spin up standalone websites for? Open a new subbrand.example.com subdomain for each.
To build on this last point, let’s pivot into the many use cases for subdomains.
Subdomain Use Cases
If you intend to incorporate additional features into your website — like a store, a forum, a blog, etc. — employing a subdomain can effectively separate these areas from your main website.
Let’s dive into some examples.
Mobile Optimization
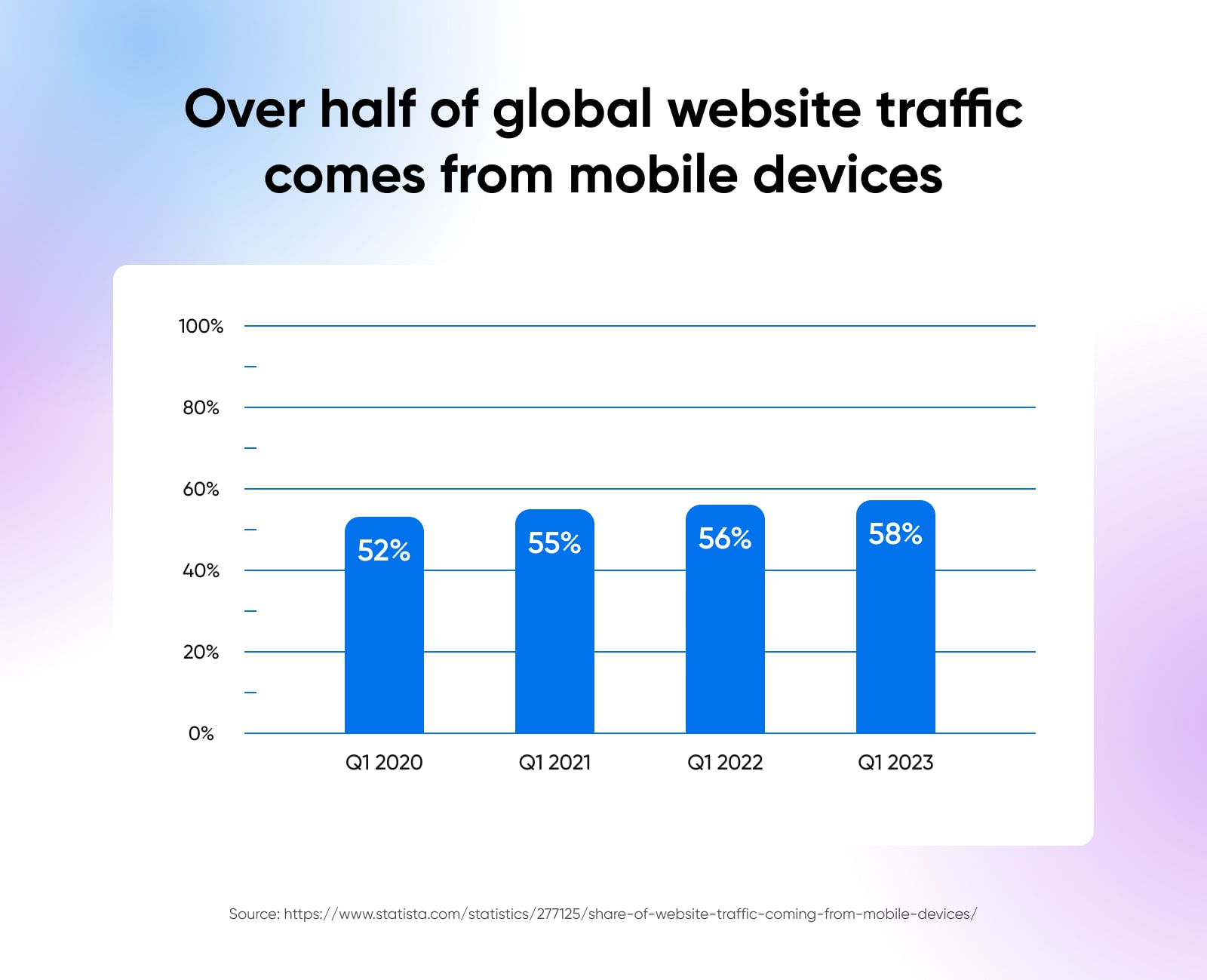
Mobile subdomains such as m.example.com prove valuable in providing a mobile version of your website for visitors on their smart devices.
Crafting tailored experiences for your mobile experience is crucial, given that well over half — and growing — of website traffic today is coming from mobile devices.
Website Staging
Another prevalent use of subdomains involves creating a testing or staging version of a website, like staging.example.com.
Developers and savvy website owners and operators commonly utilize subdomain staging sites to test new plugins, features, and other updates to make sure they work flawlessly before deploying them to the version of the website that’s live on the internet.
Ecommerce Functionality
Establishing an ecommerce store is a frequent application of subdomains.
This approach is often chosen because the store owner wants to use an ecommerce platform such as Shopify that already comes complete with things like integrated payments, inventory management, and so on.
In this case, they would create a subdomain like “store.example.com” that’s separate from their website and hosted by a platform like Shopify.
Location/Language
Subdomains are very often employed to provide localized content for areas that speak different languages and use different currencies.
For example, a brand that operates in various countries may have a comprehensive website at www.exampleboutique.com, but location-specific and language-specific subdomains to serve different areas, such as fr.exampleboutique.com or canada.exampleboutique.com.
Different User Types
Subdomains also offer the flexibility to cater to a distinct subset of users on your site.
For example, you might offer access to educational resources at student.example.com, to a login portal at user.example.com, or to a community forum for your customers at forum.example.com.
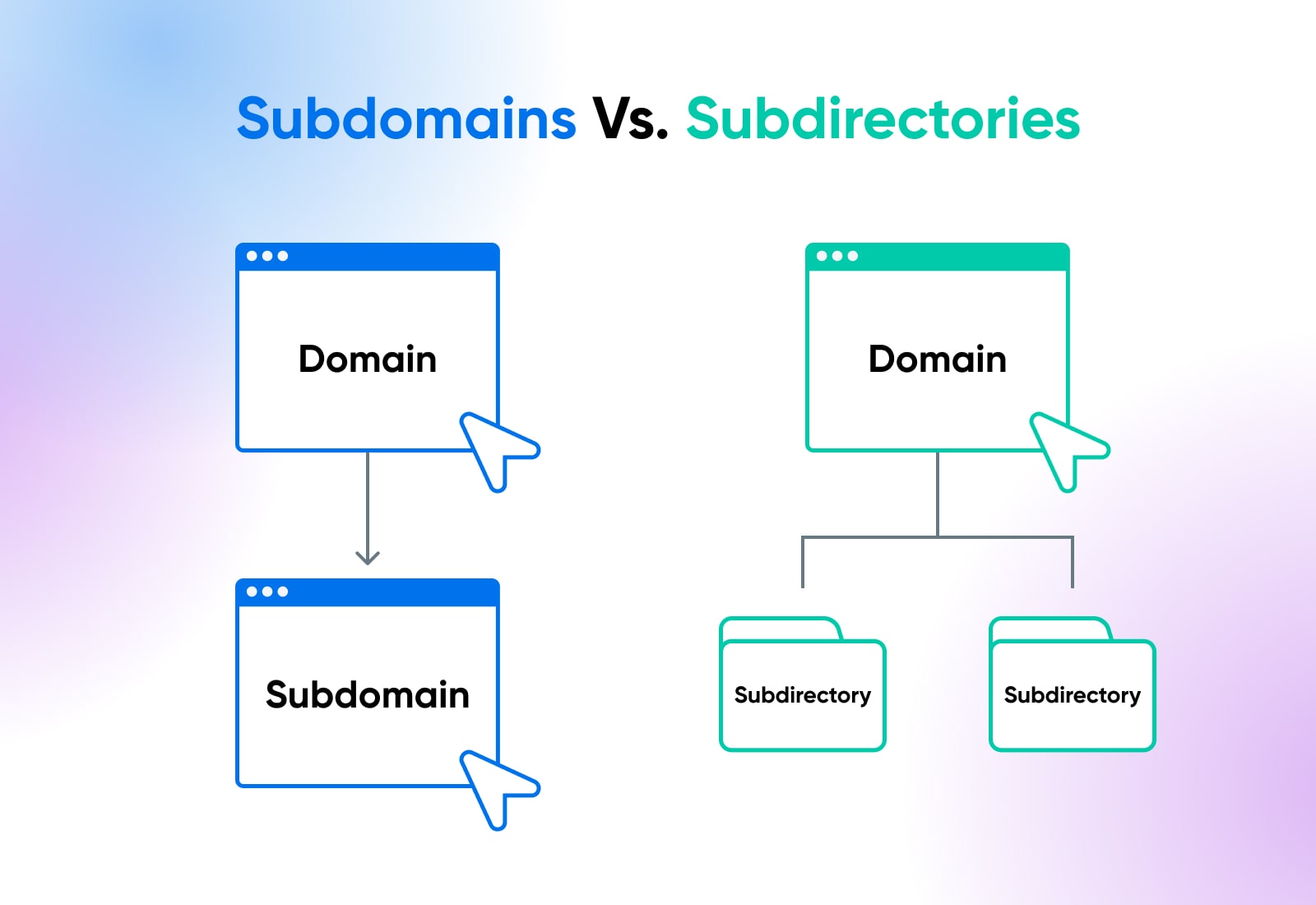
Subdomains Vs. Subdirectories (AKA Subfolders)
Subdomains are different from subdirectories (or subfolders) in that they appear as a separate entity within the domain.
A subdomain can almost be thought of as a separate website that happens to fall under, meaning it is “owned by,” a root domain in the domain hierarchy scheme.
Subdomains are indexed by search engines separately from the primary domain and any of its other associated subdomains. This means that when creating content for a particular subdomain, you should focus on optimizing it independently from the rest of your website’s content to maximize its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
In contrast, subdirectories exist under the same root domain on the website where they’re hosted. For example, if the URL of a website is example.com, then its subfolder could be located at example.com/subfolder/. Subfolders do not have their own independent indexing by search engines and do not require optimization separately from the main page.
Are Subdomains Or Subdirectories Better?
Which of these structures you should choose when adding new features or content to your website ultimately depends on your goals.
Because of the structure noted above, subdomains are usually most suitable for content that significantly differs from your main website. For example, when the subject matter serves a distinct purpose or necessitates a specific set of features (like an ecommerce shop would) compared to the rest of your site.
This means subdirectories may be better for content closely related to your main website. For instance, it may make sense to use a subdirectory to set up something like a pricing page, which has distinct content but is closely related to the rest of your website — and is something you want to make sure visitors can easily see and access. For example.com, a pricing-focused subdirectory may look like “example.com/pricing.”
When it comes to search engine optimization (SEO) specifically, most pros advise going with subdirectories over subdomains.
Related: What Is SEO?
This is because subdirectories benefit from the established authority of your root domain, which you’ve hopefully cultivated by earning backlinks and continually creating and optimizing content. Because of their attachment to your root domain, subdirectories can pretty quickly start being recognized by search engines and growing in rank compared to subdomains.
That’s because Google treats subdomains much like distinct websites. It usually can tell they’re related, but a subdomain doesn’t inherit much, if any, authority from the root domain that owns it. It’s basically like starting from scratch on the SEO front, and any recognition earned by related subdomains and root domains does not transfer back and forth.
Because of all of the above, a good rule of thumb to follow is to use subdirectories if improving SEO is your goal and to use subdomains if growing your reach is your goal.

Getting Started: How to Set Up A Subdomain
Setting up a subdomain is a relatively straightforward process, but it can vary a good bit depending on the website host and registrar you are using. Keep in mind these services can be packaged together or sold separately, in which case you’ll have to go to different portals to get everything done.
That said, these instructions should help get you on the right path.
1. Make Sure Your Hosting Provider Supports Subdomains
To begin, of course it’s essential to make sure your hosting plan will accommodate a new subdomain!
This should be easy to figure out by checking out the language in your hosting contract, poking around inside of the hosting client portal, or simply reaching out to your host.
2. Figure Out Your Name
Next, you want to determine the name of your subdomain. The next section on Subdomain naming conventions and best practices is full of tips for choosing a name that’s pleasing for both people and search engines.
3. Configure The Rest Via Your Web Host Customer Dashboard
Unfortunately, this is where we can no longer provide the specifics, as the flow here will depend greatly on your web host and registrar.
Generally speaking, you’ll need to access your domain name settings page and input the new subdomain into the “subdomains” field. Depending on the registrar, it may be necessary to manually enter an IP address for your subdomain as well. Once saved, a new CNAME record will be created in your DNS records with your new subdomain prefix pointing towards the main domain.
Interested in seeing how this process plays out in more detail? Then don’t miss our helpful instructions for two different ways to add a subdomain using DreamHost.
Related Subdomain FAQs:
Is A Subdomain Free?
|Today, acquiring subdomains doesn’t typically incur additional costs if you already own the domain name to which you wish to attach them. However, some hosting plans may still charge an extra fee for subdomains. At DreamHost, subdomains are free with our Shared, VPS, and Dedicated hosting plans.
How Many Subdomains Can I Set Up?
The number of subdomains you can have within a single root domain is limited only by your hosting provider. For context, at DreamHost we allow for unlimited subdomains with Shared, VPS, and Dedicated hosting, so you can let your creativity soar.
If you’re concerned about cost and other limitations, be sure to check with your hosting provider to get the details on your plan. And if you’re not happy with what you learn, DreamHost also makes transferring your domain to our service a piece of cake.
Subdomain Naming Conventions & Best Practices
Finally, let’s discuss how to maximize your subdomains to make sure they’re performing at their highest level.
Keep It Contextual
First and foremost, subdomains should be named in a way that is both relevant and meaningful to humans. Don’t let the desire to please our search engine overlords cause you to come up with subdomain names that are heavy on keywords but light on common sense.

A good practice for naming subdomains that walk this line is to use simple words and phrases related to the content on the page, such as “blog” or “tutorials.” This will make it very easy for people to know what to expect and for search engines to categorize and index your content.
Make It Easy To Read
Wherever possible, it’s beneficial to keep your subdomain names short and descriptive, so visitors can easily recognize them. For example, a subdomain about marketing could be named “marketing” instead of “the-complete-guide-to-marketing.”
Additionally, avoid using numbers or special characters in your subdomain name as these can be difficult for people to remember and type into their browser.
Do Your SEO Research
Chances are you’re going to want some eyeballs on your new subdomain.
When working to drive traffic to new subdomains, the same principles apply as for driving traffic to any other website or page. This includes researching and using keywords relevant to your industry that people are likely to use when searching online and optimizing metadata and quality content on each page accordingly. Additionally, building link authority by earning backlinks from reputable sources can help increase visibility in SERPs.
Related reading: Improve Your Rankings Using These 20 SEO Techniques
Don’t Compete With Yourself
A common mistake is creating multiple subdomains that are too similar or even identical to each other or to the content at your root domain.
This can cause what’s known as cannibalization in SEO — where your content starts competing with itself for ranking because you’re targeting the same phrase on different pages or subdomains of your website.
It’s important to ensure that each subdomain you create has unique content and serves a distinct purpose from any other related domains or pages.
Configure Subdomains In Google Search Console
Don’t forget to set up subdomains as separate properties in Google Search Console so you can take full advantage of the search engine optimization and reporting features available for each subdomain.
For instructions and tips on how to pull this off, check out Google’s guide.
Ready To Start Exploring Subdomains?
Prepared with insights into their purpose, benefits, and real-world applications, we hope you now feel well equipped to make strategic decisions as you embark on your journey of creating new subdomains for your website.
Love the idea but way less excited about actually stepping through the technical aspects of getting a subdomain up and running?
You’re certainly not alone.
Busy website owners and managers like you are why we created a variety of hosting plans that let you choose the level of support you need, as well as a suite of pro services where you can engage one of our experts for help with website development, management, design, and even marketing efforts.