What Is ICANN?
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is a non-profit organization that develops and enforces policy on the internet’s identifiers. ICANN manages the registration of DNS registrars and is responsible for handling domain name disputes.

More About ICANN
Though many people have probably never heard of the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), it’s actually pivotal to why the internet is as secure, accessible, and functional as it is today.
Interested to learn more about this somewhat uncelebrated element of the modern internet?
Then come along on this comprehensive guide to ICANN where we’ll cover its history, what it looks like today, and what it has to do with the domain names, domain name system, IP addresses, and root servers that make websites work.
What Is ICANN?
ICANN is a private, non-profit public benefit corporation (for generating social and public good) made up of people from around the world who are dedicated to keeping the internet predictable, usable, and secure.
We feel it’s important to note as we’ve seen some confusion on this topic that ICANN (pronounced “eye can”) is a business, not a volunteer organization. Its staff is paid and its board members are eligible for compensation.
Where does the money come from?
The wide world of website owners!
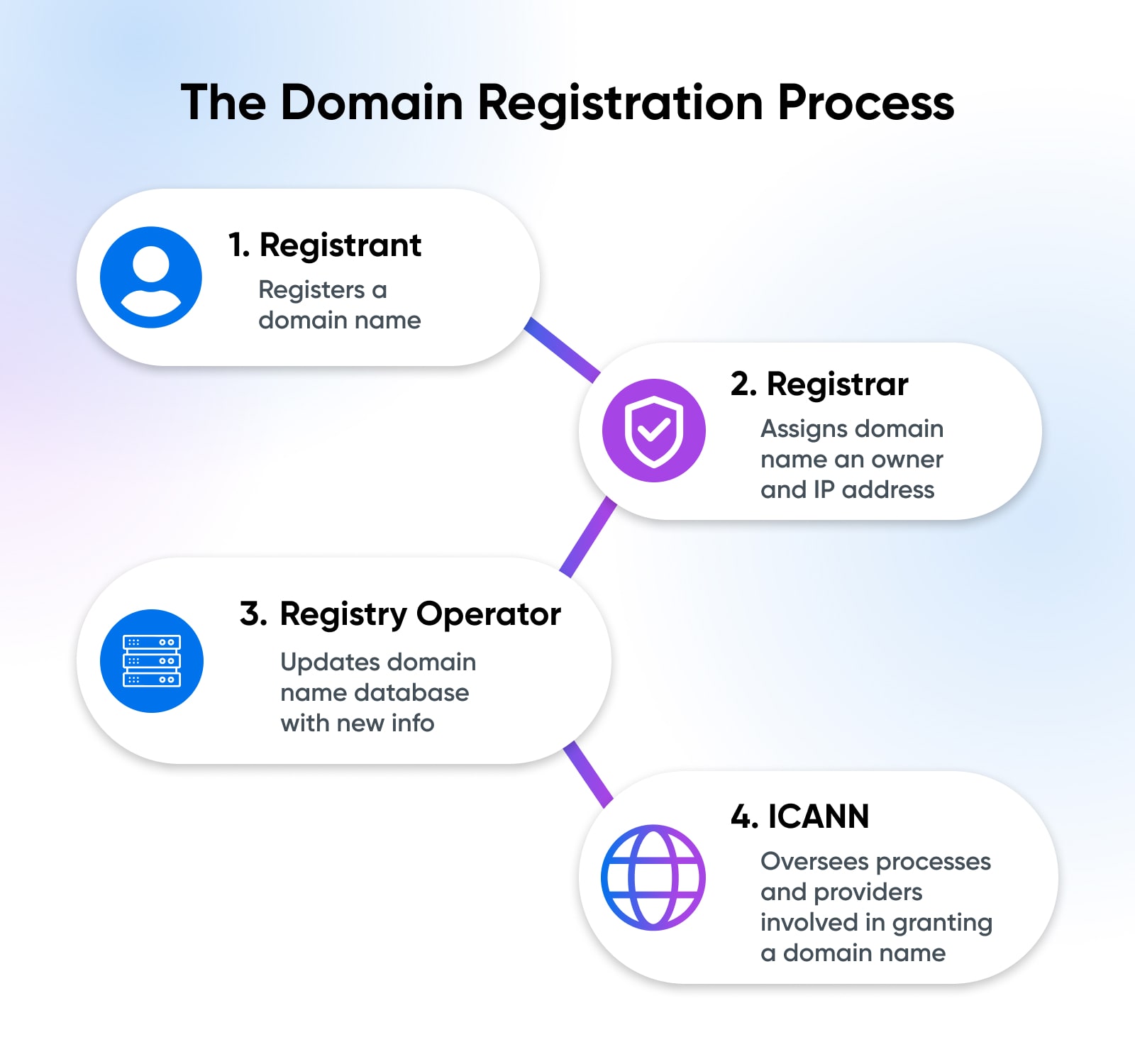
ICANN’s income comes through various sources: the registration of top-level domains; the sales and renewals of domain names to registrars, who distribute domains to the public; and the accrediting of these registrars.
Related: What is a Domain Registrar?
ICANN “controls” domain names in the sense that it oversees and governs a large network of trusted domain registrars. It sells them domain names and they then sell those domains to hopeful website owners, at a profit.
If this doesn’t make a lot of sense yet, just stay tuned. After some background, we’ll walk through the technicalities of how ICANN interacts with, but never single handedly controls, core pieces of the modern internet.
A Brief History Of ICANN
In the beginning there was just Jon Postel, a computer scientist who kind of fell into being in charge of distributing domains and IP addresses.
In 1998, the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) from the U.S. Department of Commerce (DOC) released a proposal for policy to help grow, manage, and privatize this process. Later in 1998, this led to the formation of ICANN, which was to manage the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) under the DOC.
ICANN was the purview of the American government until a historic agreement in 2016 removed DOC oversight from ICANN. Originally operating from the same building where Postel made his contributions to the internet in Marina del Rey in Los Angeles County, ICANN’s headquarters have moved but are still nearby in Playa Vista, California.
What Does ICANN Do?
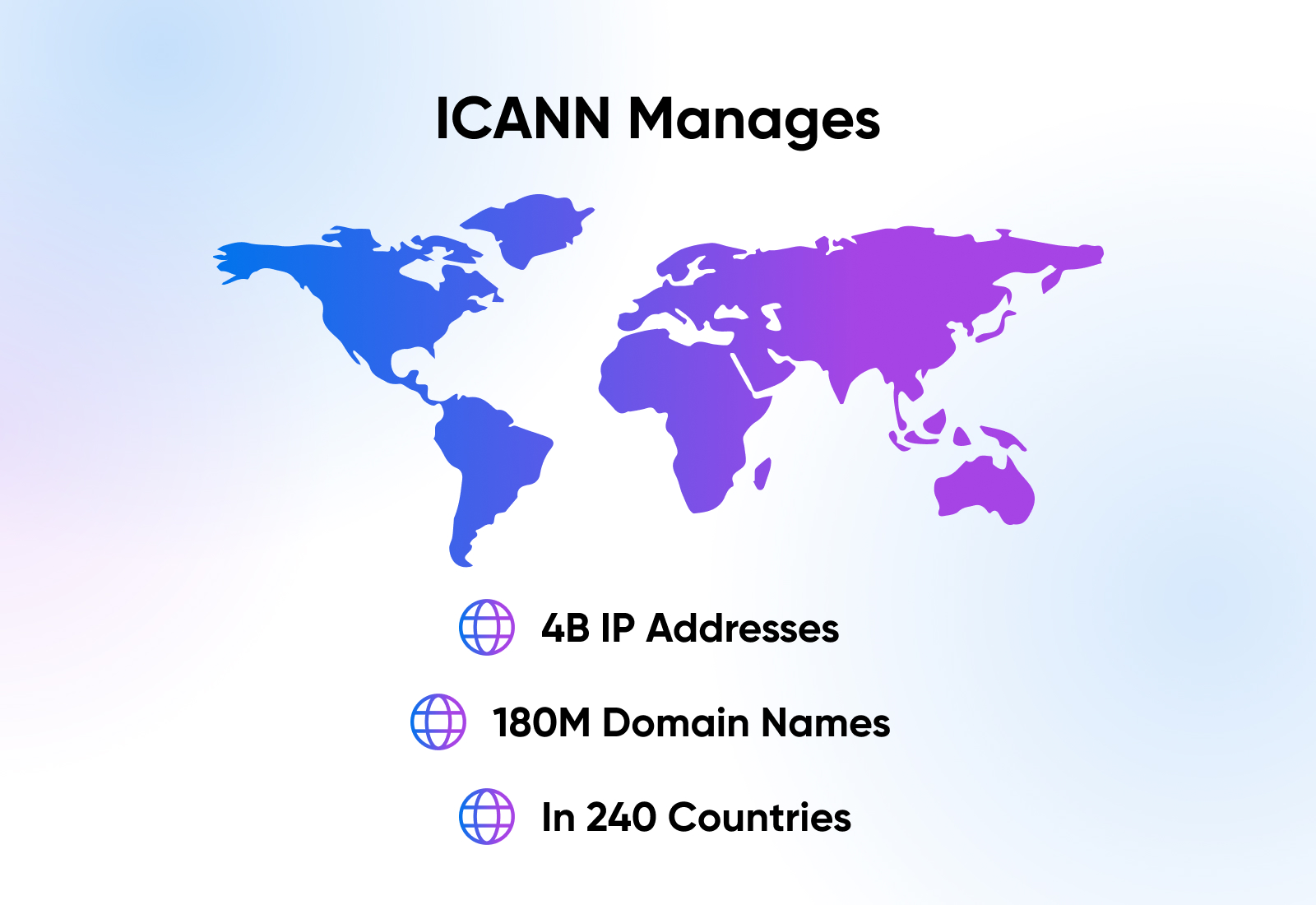
To greatly simplify things, you could say they oversee the unique identifiers that make it possible for us to type something like “https://www.dreamhost.com/” into an address bar and arrive at the intended destination every time.
More specifically, they help manage the repository for IP addresses, the root server network, and the domain name system in order to get this done.
Note that this does not mean they control access to or the the content on the internet — a topic we’ll get into more later on when we discuss whether or not ICANN can shut down your website (Spoiler, nope!).
Overall, ICANN manages millions of domain names and billions of IP addresses all over the globe.
With that, now let’s get into the nitty gritty of how ICANN interacts with the different elements that make modern websites tick.
ICANN, Domain Names, & DNS
Computers speak in numbers, so they locate websites on the internet using IP addresses. To make navigating the web easier for individual internet users, domain names like ours, dreamhost.com, are attached to these IP addresses.
The domain name system (DNS) keeps track of connected domain names and IP addresses. As you can see, all of these elements are closely intertwined, so it makes sense that ICANN would play a part managing each one of them.
Related: What is a Domain Name?
The main parts of domain names that ICANN deals with are the second-level domain (SLD) and top-level domain (TLD).
SLDs are usually branded and unique. The SLD for dreamhost.com is “dreamhost.” The TLD is the .com.
TLDs come in categories that help users understand their location, goal, age, operator, and more:
- Generic top-level domains (gTLDs): .com, .org, .net
- Country code top-level domains (ccTLDs): .uk, .ca, .fr
- New top-level domains (nTLDs): .agency, .bio, .charity
- Sponsored top-level domains (sTLD): .google, .apple
What does ICANN have to do with domain names and the DNS?
ICANN manages SLDs and TLDs with help from the Generic Names Supporting Organization and Country Code Names Supporting Organization. These are a few of the many bodies inside ICANN which offer policy advice.
ICANN mostly does this by managing a network of accredited domain registrars (including DreamHost!), which adhere to and help spread its policies as they sell domains around the world.
To find out more about registrars, learn which ones are accredited, file a registrar compliant, and more — check out the Network Information Center, which is operated by ICANN.
Related: What is DNS?
ICANN & IP Addresses
To humans, IP addresses look like strings of numbers and sometimes letters, separated by dots or colons based on how old they are. For example, an IP address for one of DreamHost’s nameservers is 162.159.26.14.
An IP address identifies a unique device and which network it’s on, enabling other devices to reach and communicate with it.
ICANN manages the supply of IP addresses in the central repository, which is divided into five Regional Internet Registries around the globe. It does this with the help of the Address Supporting Organization, another ICANN advisory committee that makes recommendations and supports the board on IP address decision making.
Related: What is an IP Address?
ICANN & Root Servers
The root zone is the core of the DNS hierarchy. It contains 13 root servers, which handle domain name requests for different different top-level domains.
IANA, which became a department of ICANN with its formation in the ‘90s, oversees the DNS root zone. It does this mostly by doling out management responsibilities of each root server to different organizations.
Interested in learning more about root servers and their role in DNS? Take a deep dive into all things DNS with our guide What Is DNS?
Why Does ICANN Matter?
At this point you probably have a pretty good idea of why ICANN exists, and thus why it’s an important organization.
We’d sum it up by saying ICANN matters because it provides a centralized authority with the organizational structure and managerial power to keep the internet pretty secure from bad actors and accessible to website owners and everyday users.
Because of the policies ICANN has developed and worked to enforce over the years, the internet works how we’d expect it to on any given day — no matter where we are in the world, what our income level is, or what kind of device we’re using.
This concept is called “universal resolvability” and it has never been more important than it is today. Many people’s entertainment, employment, and even connection to loved ones requires internet access.
Can ICANN Shut Down A Domain?
Simply put, no.
The role of ICANN is not to directly manage domain names. Rather, it works to establish rules that trustworthy domain name registrars strive to follow when they grant domain names as part of the domain name registration process.
What ICANN can do is remove accreditation from a registrar, which it did recently when one abused its role by handing out domains to bad actors.
However, the registrar who sold you your domain name can take it down. Usually, this only happens when a domain is being used to spread harmful content, conduct scams, etc.
That’s why ICANN always suggests working with domain name registries they recognize on their List of Accredited Registrars. (Note: At this point, most registrars are accredited by ICANN, and those that aren’t are usually just resellers working with an accredited registrar.)
ICANN lacks the authority, both technically and legally, to remove domain names from the internet. If you find your domain acting up, your first stop should be your website host and then your registrar, if they’re separate entities.
Who Makes Up ICANN?
As you would probably expect from an organization that has grown over the years to keep up with the exploding usage and capabilities of the internet, there are a lot of moving parts within ICANN.
We’ll start with what are known as the supporting organizations, which have been mentioned here and there already throughout this article: the Address Supporting Organization, Country-Code Names Supporting Organization, and Generic Names Supporting Organization.
Next are four advisor committees that come together to represent the internet community, organizations who need trustworthy security on the internet, root server managers, and of course international governments and treaty organizations.
The ICANN board of directors as well as non-voting liaisons are chosen by these groups as well as the independent Nominating Committee. Learn more about these groups and other elements of what’s known as the ICANN community here.
While the structure of the aforementioned board of directors can change, at the time of this writing it’s made up of 16 voting Directors and 4 non-voting liaisons. The board includes the chair, vice-chair, and president and CEO of ICANN. An ombudsman sits outside of the board as an independent party that handles any complaints about ICANN.
And last but certainly not least, there are hundreds of hard-working staff members around the world who carry out ICANN’s policies, act on its needs, and overall keep the ship sailing.
Who Controls ICANN Now?
At the time of this writing, Sally Costerton is the interim president and CEO of ICANN.
The ICANNWiki is a really interesting third-party source of information if you want to keep your finger on the pulse of all things ICANN, including the makeup of the board at any given point.
Who Holds ICANN Accountable?
According to ICANN itself, there are several layers of accountability that help keep the organization on task and above board in its operations.
First, as it’s established under the laws of both the State of California and the United States, it’s beholden to both state and federal laws. And, as what’s considered a “non-profit public benefit corporation” it also must adhere to the rules governing corporations.
In addition, there are internal systems built into the ICANN network helping ensure there are checks and balances. First of course are the bylaws which regulate its actions. There’s the board itself, which is made up of representatives from around the world who are selected by the organizations named above and ordered to act in the best interest of ICANN. Senior staff outside of the board, but often reviewed by the board, provide another point of view and oversight. Finally, ICANN has several resolution procedures that include consulting the board as well as an independent review panel in the case of a debate over a decision.
If you really want to explore this topic, ICANN has a robust page all about accountability on their website.
Even with these measures in place, there are those who are concerned with the power ICANN holds. The most common complaints are that a singular, private company shouldn’t have such heavy control over core pieces of internet functionality; that the domain name registration pricing set by ICANN restricts creativity and small business; and that its origination within the U.S. government still influences the group to make American-centric rulings.
Inspired To Register Your Domain Name?
Perhaps ICANN’s biggest impact on the modern internet is how it has standardized and secured the process of granting domain registration to the website owners who help us conduct our businesses and live our lives every day.
Have you had a business idea for a while and need a domain name to get your website started?
It’s easier than ever with tools like DreamHosts’s domain name search and registration flow.
We make managing your website easy with free subdomains, simple domain transfers to get all your properties under one roof, an easy-to-use dashboard, fully managed hosting, and even access to pro service providers who can take your website to the next level with design support, development help, marketing assistance, and more.