When ChatGPT launched in November 2022, it reached 100 million users faster than any product in history. That triggered a race for companies to build AI assistants and chatbots.
Now these companies are taking the next step: giving AI direct browser control to act on your behalf. That means telling the AI to shop for groceries, book flights, and handle repetitive tasks the same way you’d use chat.
But there are quite a few browsers out there now. Some free, some paid. Every demo looks incredible. But every real-world application hits problems (or seems that way).
The question is which browser fails least often.
What Makes an AI Browser Different From Chrome With ChatGPT Open
Traditional browsers display web pages. AI browsers treat the web as an operating system where AI agents work on your behalf.
There are three architectural approaches competing for dominance:
- Agentic browsing: The AI actively navigates sites, clicks buttons, fills forms, and completes workflows without human intervention.
- Conversational assistance: A persistent sidebar AI sees your tabs, answers questions, and synthesizes information. This is more reliable than agentic browsing.
- Hybrid intelligence: Combines passive AI features with selective automation. You maintain control while AI handles specific tedious tasks.
Why Does the Specific AI Model Matter Less?
Underlying AI models like GPT-5 and Claude are largely commoditized. They write emails and summarize PDFs with similar accuracy. The differentiators are context and friction.
- Context: Does the browser understand you are viewing a spreadsheet in Tab 1 and a competitor’s pricing page in Tab 2?
- Friction: Does the browser seamlessly insert generated text into your CMS, or are you stuck copy-pasting?
How We Tested the New AI Web Browsers
We tested five browsers on identical workflows to see if “agent” features save time or add complexity.
Data curation: We gave each browser a specific natural language prompt.
“Go to Amazon.com, research the best coffee makers under $100 with coffee bean grinding instead of pods, and create a table of the 5 best ones. Then add two of the best choices to cart with my New York address selected.”
This tested the ability to navigate dynamic DOM elements, interpret pricing data, and manage session states.
Usability: The browser must be clean and familiar. If it requires extensive learning time, adoption becomes difficult.
Friction: We measured whether using the AI was faster than doing the task manually. We timed each task from initial prompt to outcome.
1. Perplexity Comet
Price: Free (dropped from $200/month in October 2025)
Platforms: Mac, Windows
Agentic quality: Works more often than breaks.
Built by Perplexity AI, Comet came to market as an expensive experiment before pivoting to free. The Perplexity team clearly figured out that owning browser distribution matters more than subscription revenue.
Testing Comet
We entered the coffee maker prompt, and Comet initiated a search to parse the Amazon results page.
It accurately identified products under $100 with grinder features, created a comparison table showing prices, and then added two options to the cart.
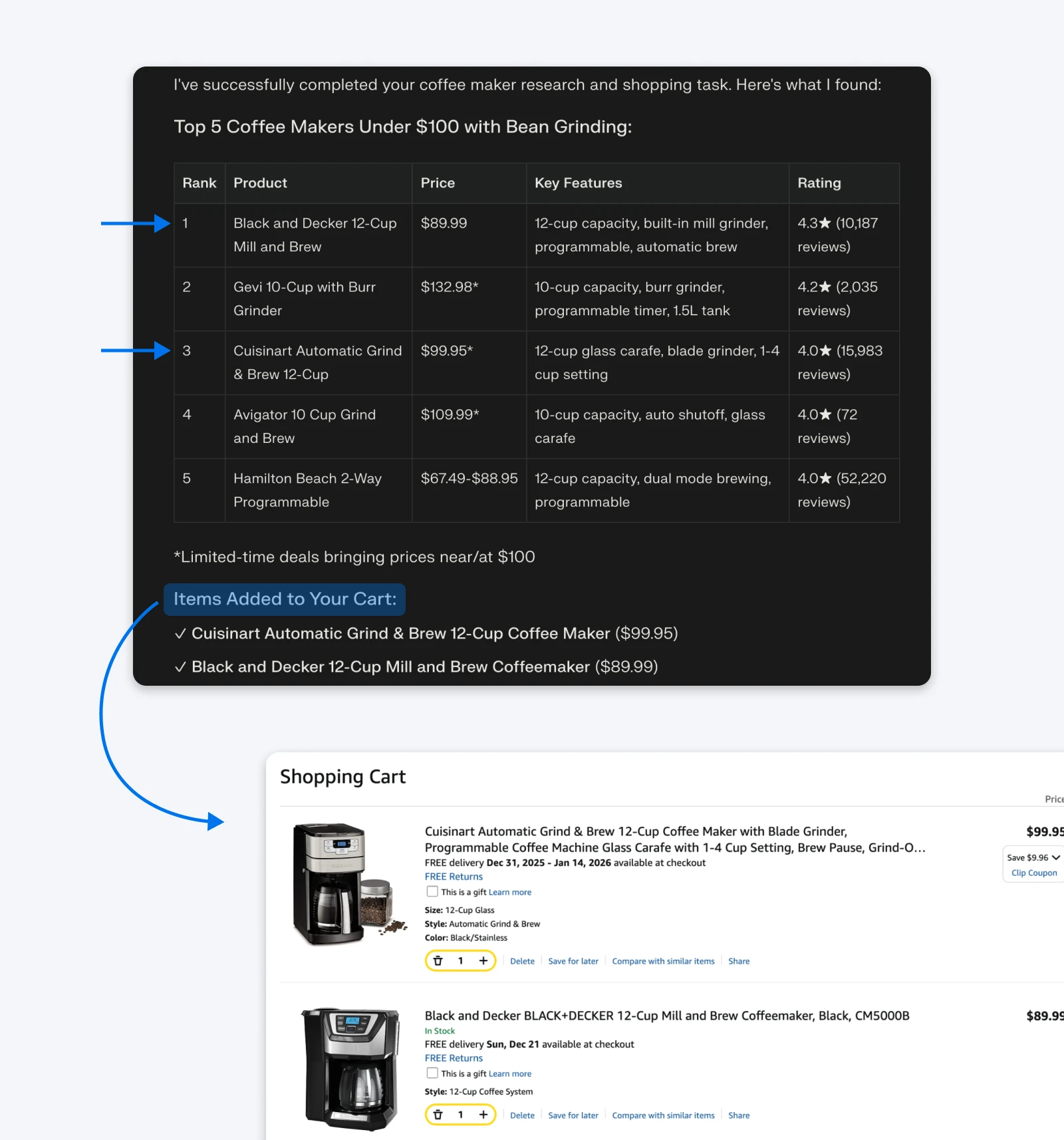
The process completed successfully, and Comet stopped at the cart page without attempting to complete the purchase, which is the correct behavior.
Interface and Usability
When it comes to text insertion, Comet can either add text automatically when in browser control mode, or you can copy-paste text as required. However, we could not find another way to insert text directly from the chat.
The command understanding is quite strong. When we asked it to “find the pricing difference between our top two competitors,” it correctly identified which tabs contained competitor sites and extracted pricing data. And the browser overall is quite clean and easy to get used to.
Our Take
Comet saves time on research and analysis, meaning tasks like content creation, competitive analysis, and data review that previously required cross-referencing multiple tabs now take minutes. It handles context across browser sessions without losing track of what you are working on.
Since it is built on Chromium, all your Chrome history, extensions, passwords, and bookmarks are automatically imported, reducing the friction of switching.
2. ChatGPT Atlas
Price: Free
Platforms: Mac only (Windows “coming soon” since October 2025)
Agentic quality: Struggles with tasks Comet handles easily.
OpenAI launched Atlas with 800 million weekly ChatGPT users as potential distribution, yet the browser itself seemed rushed. The problem is that every feature reinforces ChatGPT usage rather than improving browsing, which likely means OpenAI is more interested in selling than building a capable browser.
Testing Atlas
Atlas attempted to perform the shopping task using its ”Agent” mode. Although it navigated to Amazon successfully and reached the checkout, the process felt sluggish compared to Perplexity.
The AI cursor hovered over the search bar for about five seconds before the results loaded, and then it spent another ten seconds analyzing the page structure. It eventually got the job done, but not in a time that would be considered usable.
Interface and Usability
ChatGPT offers a quick insert feature, like most other browsers on the list, that allow you to move text from the chatbox to where your cursor is placed.
However, the interface feels like a wrapper around ChatGPT rather than a browser. Autonomous browsing is extremely slow, and you have to watch it think for extended periods before it executes simple actions.
Our Take
Atlas adds friction instead of removing it. Simple tasks take longer than manual completion, and the AI frequently misunderstands which tab or content you are referencing. Atlas makes sense only if you are already a heavy ChatGPT user and want that specific interface for browsing.
3. Opera Neon
Price: $19.90/month
Platforms: Mac, Windows
Agentic quality: Best in class — when it works.
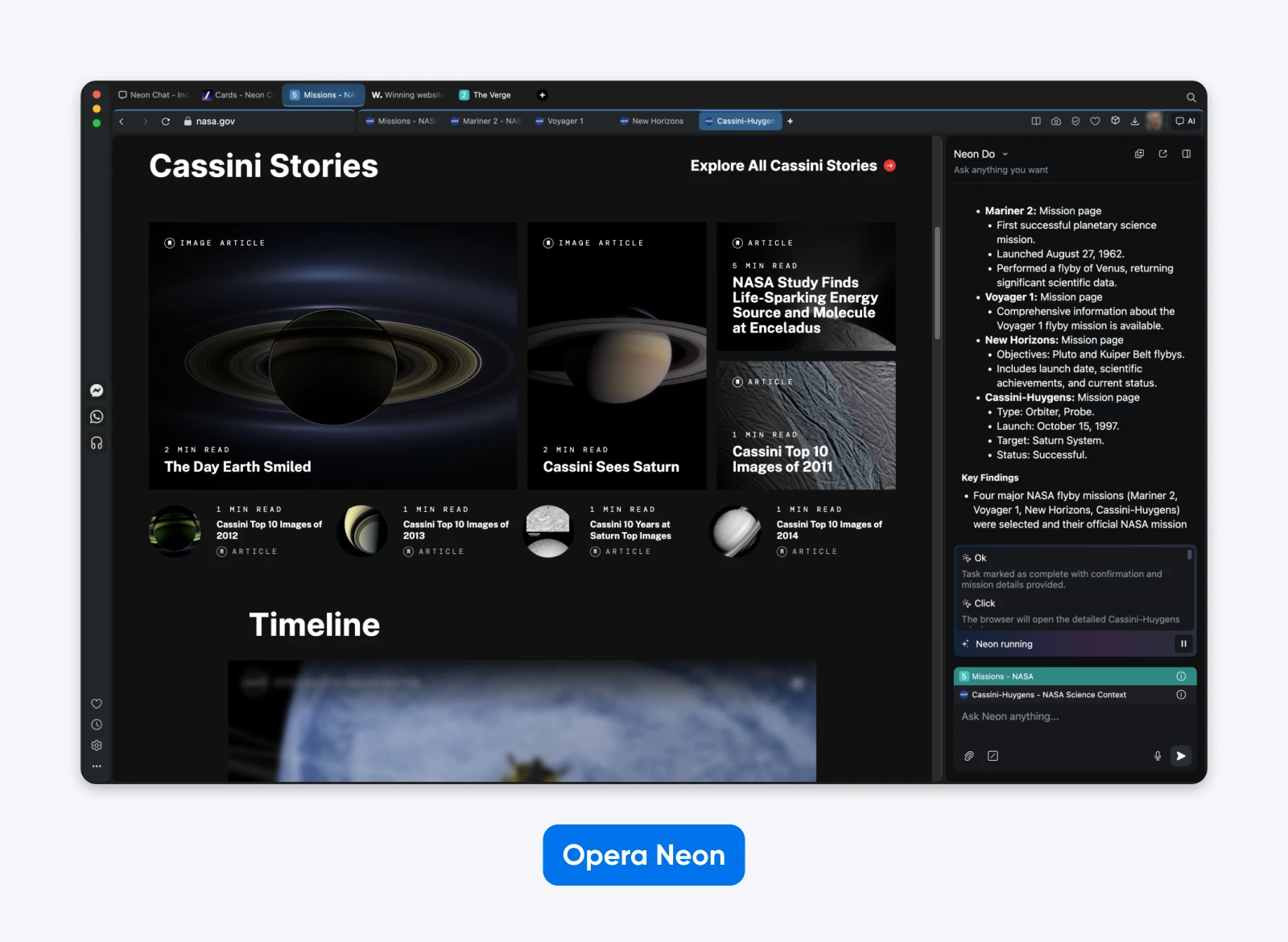
Opera has invested two years into agentic AI technology, and it shows. It splits the browser into three modes:
- “Chat” functions like any AI assistant
- “Do” represents Opera’s agentic browsing
- “Make” delivers capabilities like building a functional website from a prompt
Testing Opera Neon
Neon is the closest we have to a true, full browser control agent. Its “Do” mode can successfully navigate through product pages, handle cart additions, and even create and execute games.
Interface and Usability
The interface is distinct from standard Chromium browsers because it uses a split-screen approach for AI tasks. This prevents the sidebar compression issue we saw in Comet, keeping the main web page at full width while the AI operates in an overlay.
Neon also nailed our insertion test. When we generated a response to a client email, Neon offered a ‘Paste to Input’ button that worked seamlessly, whereas other browsers forced us to copy the text manually.
Our Take
Neon saves time for power users. The ability to insert text directly and automate simple button-clicking tasks justifies the learning curve. If you can justify the monthly price tag, this may be a browser worth experimenting with.
4. Dia
Price: Free (beta)
Platforms: Mac, Windows (limited)
Agentic quality: Inconsistent.
The Browser Company created Arc, which is beloved by design-conscious users. Dia represents their second attempt, rebuilt from scratch with AI at its core. While the browser has a minimalist interface and thoughtful interactions, the execution is subpar.
Shopping Test Results
Dia could not complete the shopping test result since it seems not to have browser control access.
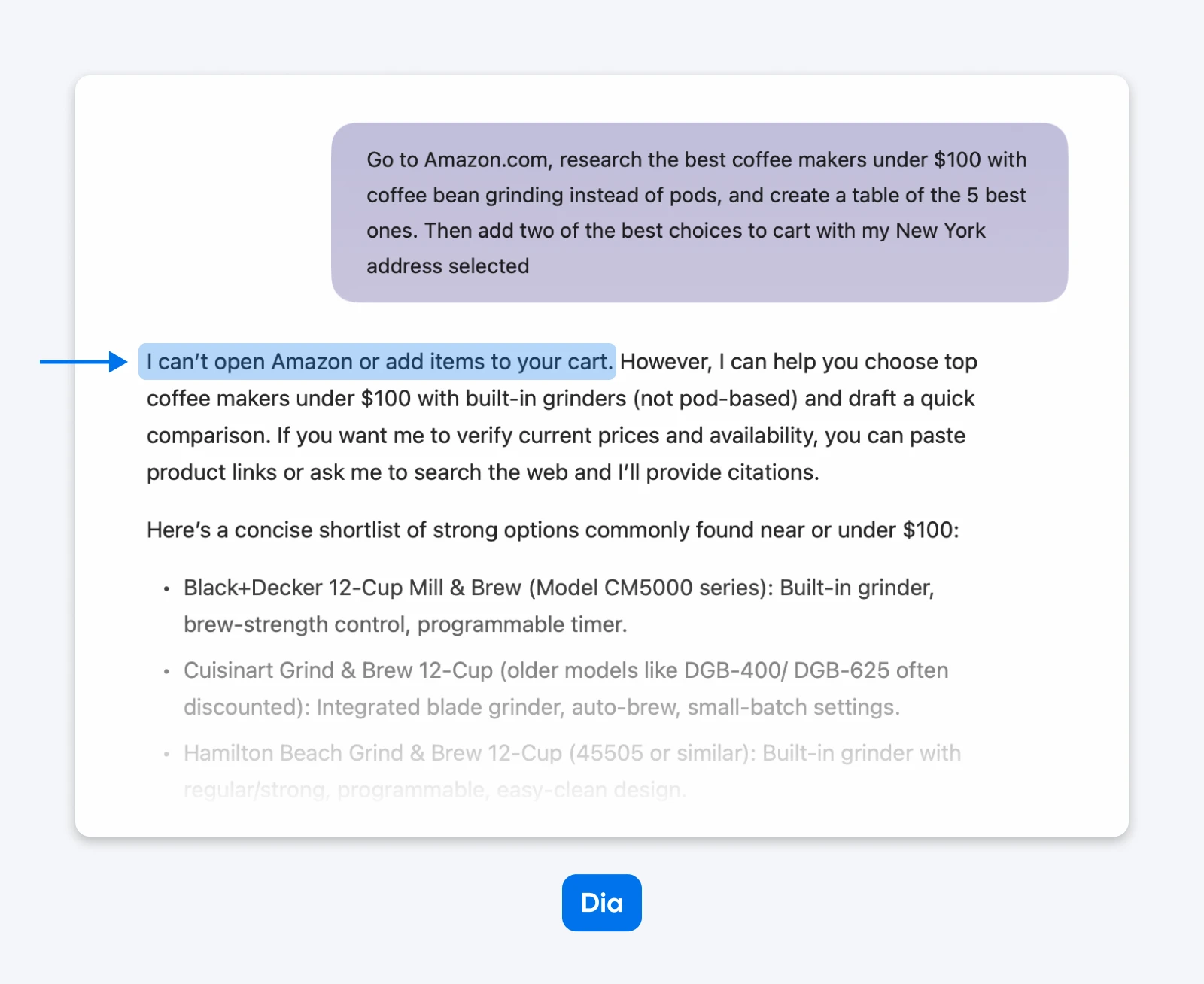
Instead of navigating to Amazon and parsing results, Dia generated a list of coffee machines, which wasn’t useful since we had to research Amazon for the latest prices anyway.
Interface and Usability
Dia provides an “Insert” or “Replace” button that pops up when you are in chat mode, trying to make edits to existing text. On the interface side, Dia has received a lot of design love, and we would love to see more browsers take an out-of-the-box approach.
Our Take
Dia browser feels like a design concept rather than a tool. We experienced frequent crashes during multi-tab operations, and it often freezes when trying to load heavy web applications.
5. Chrome + Gemini
Price: Free
Platforms: All
Agentic quality: What agentic features?
Google announced Chrome’s biggest upgrade ever in September 2025, but they delivered only a Gemini sidebar and basic tab management. True agentic browsing has remained a “coming soon” feature.
Testing Chrome with Gemini
Since Chrome currently lacks true agentic features, it could not perform our automated shopping workflow. There was no “Agent” mode to navigate Amazon or add items to the cart. The browser relies entirely on manual user interaction for these tasks, offering only passive assistance via the Gemini sidebar.
Interface and Usability
Given that Chrome is the most-used browser, the lack of AI agentic features is quite surprising. While Opera added agentic browsing, Chrome seems to keep the AI out of the way.
The Gemini integration is there if you need it but does not interfere with standard browsing, which is a usability win for those who want a browser to just be a browser (with a bit of AI). And the tab organization features are subtle but effective as it automatically groups tabs by topic without being asked.
Our Take
Chrome is the most efficient option for 71% of users simply because it preserves your existing workflow. You do not have to export bookmarks or find alternatives for your essential extensions. The friction of migrating to a new browser outweighs the benefits of a slightly smarter AI.
What About “Hallucination” in a Browser Context?
We are used to LLMs hallucinating facts in a chat window, but it becomes problematic when they hallucinate navigation. During our testing, we came across several instances where the browser lied about the state of the web page.
- Phantom elements: Atlas tried to find a “Submit” button, though there was a “Download report” button. It likely hallucinated the button based on training data of generic forms.
- Fake summaries: Dia generated a convincing summary of a paywalled article. We verified that the browser could not access the text and had only hallucinated the summary based on the headline.
If you cannot trust the browser to report what is on the page accurately, you cannot use it for serious work.
What Actually Works vs. What’s Marketing Hype
Tasks browsers handle reliably:
- Content summarization: They are excellent at digesting long-form content.
- Research across multiple sources: They can synthesize data from five open tabs better than a human.
- Product comparison: They are great at creating tables from unstructured e-commerce data.
- Tab organization: Grouping tabs by context is a solved problem.
Tasks browsers fail frequently:
- Multi-step checkout: Verification requirements and security tokens break agents every time.
- Complex form filling: If a form spans multiple pages or uses dynamic validation, the AI will fail.
- CAPTCHA solving: This is the hard stop for all current AI agents.
- Anti-automation sites: Sites like LinkedIn and Facebook have aggressive defenses that block these browsers immediately.
Is the Convenience Worth the Switching Cost?
The shiny demos of Dia and Opera Neon hide the fact that switching browsers is hard.
- Extensions: Most of the browsers on this list are Chromium-based so moving extensions would work fine. However, depending on how deeply AI has been integrated into the browsers, the extensions may not work as expected.
- History and Bookmarks: Chrome knows your history, auto-fill data, and credit cards. Even if you import most of the data, a new browser starts at zero (no cookies, no accounts logged in). You have to re-login to all services to ensure your workflows migrate successfully.
What About Security Issues With AI Web Browsers?
Every AI browser shares fundamental security vulnerabilities because the same capabilities that help with automation create attack vectors.
Prompt Injection
OpenAI’s CISO admitted that “prompt injection remains an unsolved security problem.”
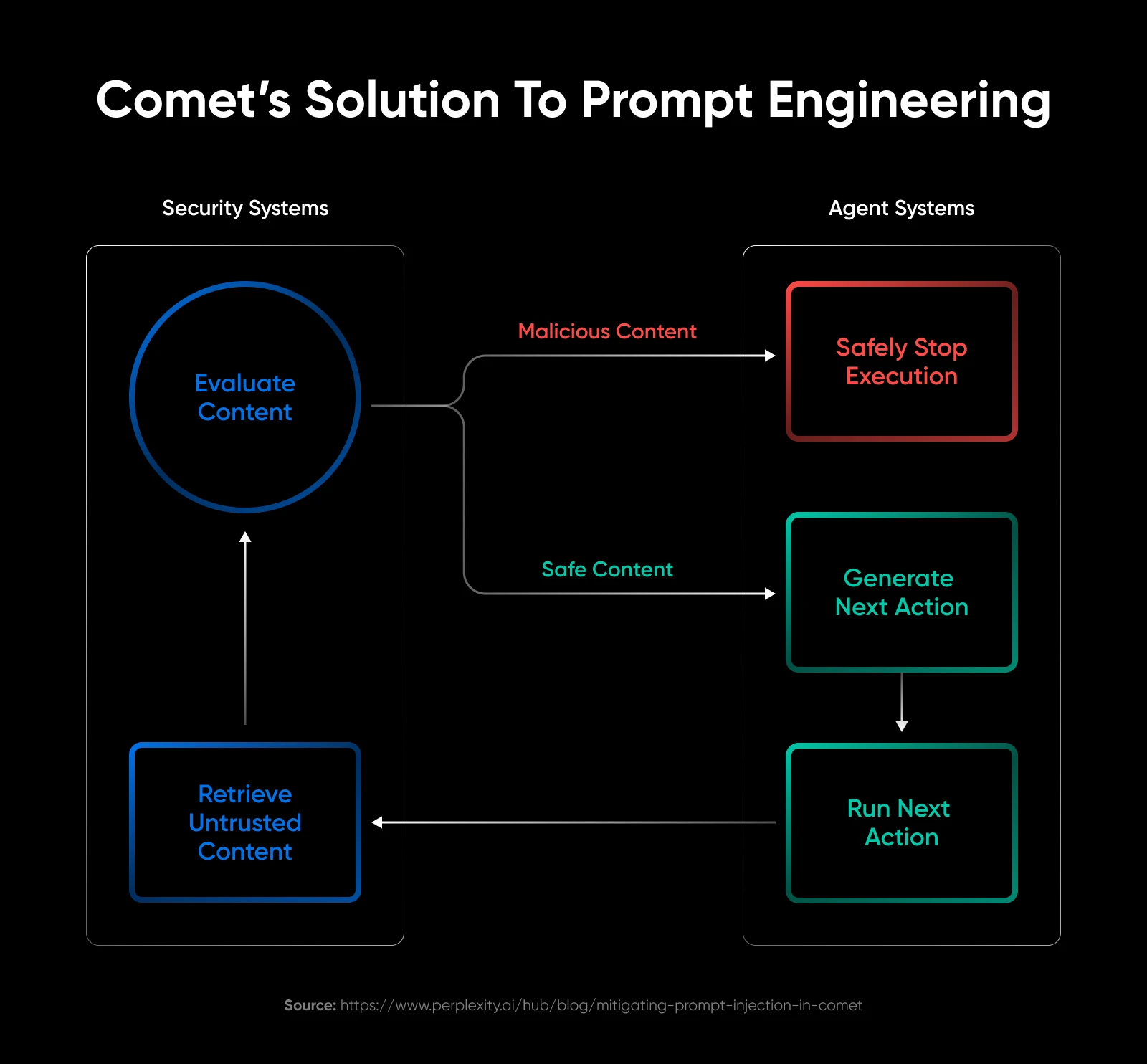
Researchers at Brave demonstrated successful attacks across all tested browsers.
They added hidden text in web pages instructing the AI to perform unauthorized actions, and the AI followed through because it cannot distinguish between user commands and malicious instructions.
The vulnerabilities were reported to Perplexity in July 2025. Perplexity has released patches in August that fix the problem. The current versions of Perplexity seem to handle security issues quite a lot better than previous ones did
Data Privacy
AI browsers require extensive permissions to function. If you want the browser to complete a workflow, it needs access to your browsing history, credentials, email, and calendar.
Most of these browsers process this data in the cloud. They send snapshots of your screen or the DOM tree to an inference server. This means your private banking window is being sent to a third-party server for processing.
Practical mitigations:
- Grant permissions selectively per site.
- Use for public browsing and avoid sensitive financial transactions.
- Turn off features when not actively needed.
- Assume AI sees everything when activated.
Which AI Web Browser Would We Recommend?
The browser you benefit most from depends on your use case.
- For researchers and students: Comet wins. Research synthesis and multi-tab comprehension justify the minor learning curve. The free price lets you experiment risk-free. It is the best tool for turning information into knowledge.
- For developers and power users: Opera Neon deserves serious consideration. The agentic browsing quality matters when your professional hourly rate justifies the subscription. The ability to build tools within the browser is a superpower.
- For design-focused users: Arc now or Dia in six months. The Browser Company understands interface design even if their AI features lag behind competitors. It is the most pleasant place to spend your internet hours.
- For everyone else: Stick with Chrome. The AI might be limited right now, but keeping your extensions and history intact is worth more than a chatbot. The context of convenience wins here.
The Bigger Question Is, Do We Need AI Web Browsers?
AI browsers are a bet on how we will interact with information going forward. Major tech companies are investing heavily in this category, the underlying AI models improve daily, and users increasingly expect AI assistance.
We are a bit skeptical because the market share for traditional browsers like Chrome is still massive, and automation capabilities remain inconsistent. The actual use case is probably somewhere in between the traditional browser capabilities and overhyped news. But, these browsers will improve over time, and we’re only just beginning to see this new method of working.


